See our latest projects and be updated with recent news and features
happening in the world of pneumatic conveying, materials handling
and industrial vacuum systems.
See our latest projects and be updated with recent news and features
happening in the world of pneumatic conveying, materials handling
and industrial vacuum systems.

Tuesday, May 21, 2024
Workplace noise-induced hearing loss is a serious problem and something not to be ignored. Permanent tinnitus (ringing or other noises in one or both ears) and hearing loss will result from exposure to dangerous levels of noise. WorkSafe Victoria in its guide on health and safety for noise estimates that more than 100,000 workers in the State are at risk of noise-induced hearing loss.
SafeWork NSW has a detailed Code of Practice for managing noise and preventing hearing loss at work. Some of the major requirements they have businesses comply with include:
Workplaces grapple with the problem of excessive noise. Effective measures can be implemented to control and reduce it. Read on to learn more about this issue and see our example of how we use enclosures to protect workers from noisy blowers.

Noise-induced hearing loss risks exist for over 100,000 in Victoria
The Code of Practice for managing noise and preventing hearing loss at work by SafeWork NSW clearly articulates who is responsible for the prevention of noise-induced hearing loss in the workplace. They make it clear that managing noise safety from any equipment or plant in a workplace is the responsibility of:
Each and every keyholder involved with workplace equipment or plant is accountable for this issue in some way. Are you aware of this?
In the SafeWork NSW Code of Practice, business owners have the responsibility of ensuring the noise a worker is exposed to at the workplace does not exceed the exposure standard for noise. Failure to do so might see them penalised for breaching the Occupational Health and Safety Act or be required to pay compensation to injured workers.
Read up on our guidelines on how noise can be reduced for equipment and plant in the workplace.
Designers, manufacturers, suppliers, importers and installers of equipment and plant have the responsibility to ensure they operate so noise emission is as low as reasonably practicable. They should also provide information about noise emission values of equipment or plant, so business owners can properly assess the risk of hearing loss to workers and implement measures to mitigate that risk.

Noise-induced hearing loss have tasks and responsibilities that span designers, manufacturers and suppliers
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has identified several industries that are a major cause of induced hearing loss amongst workers. These include the following:
Do you belong to these industries? If so, make sure you are aware of your responsibilities in regard to keeping noise levels safe for workers.
The manufacturing industry is an extensive user of roots blowers. They are used in applications such as :
Roots blowers generally emit noise at a high decibel level while working. They are limited in their ability to have effective lubrication and muffler systems installed that would help quieten their operation. The internal rotating lobes require mechanical contact and ability to freely discharge air and material into adjoining vessels and pipework.
Pneuvay Engineering does supply roots blowers that operate with noise but allow nearby workers to be exposed safely for short periods of time. To reduce the noise to allow workers to be exposed to this plant for long periods of time, we use custom designed and built roots blower enclosures. Pneuvay Engineering is also able to supply roots blower enclosures to reduce the noise emission level of your blowers.
Talk to us to learn more about it.

Business owners, designers, manufacturers, importers, suppliers, installers are all responsible for managing noise-induced hearing loss risks in the workplace
The amount of noise workers can safely endure depends on the volume of the sound and the length of time of the exposure. An exposure of 85 dB is considered standard as the minimum noise a person can endure to avoid hearing loss. In cases where noise levels go beyond 130 dB, such as impact or explosive noises from sledge hammering or gunshots, then it would take less than a second to damage the hearing of a worker.
The type of plant we typically design, build and supply uses pneumatic and compressed air. The noise level this type of plant can operate at is typically from 85 to 95 dB. This means such workers must be managed relative to their noise exposure to this plant. While workers can be exposed to 85dB for a maximum of eight hours, if the plant operates at 88dB then their exposure must be restricted to four hours maximum. If the roots blower emits 90dB then the exposure must be for a maximum of two hours.
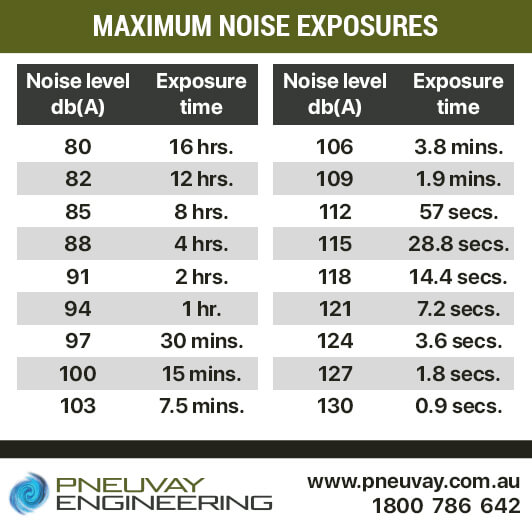
Maximum noise exposure workers can endure in the workplace
The degree of noise experienced by workers depends on the industrial process with which the worker is involved. There are several industrial processes that are renowned for having high noise levels from 85 dB to 107 dB.
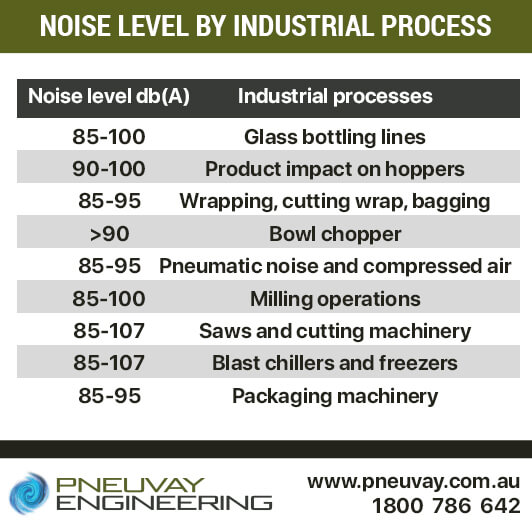
Noise level by industrial process
Ideally, noise should be kept at 85 dB or lower to ensure exposed workers will not suffer noise-induced hearing loss. When exposed to equipment and plant that emit higher noise levels, the maximum time of exposure is anywhere from four hours to just a couple of minutes. The level depends on the industrial process. Noise is considered extremely dangerous when it is beyond 91dB and exposures have a maximum of two hours or less.

When is noise dangerous - beyond 91dB is extremely dangerous
Technically speaking, there are two ways of minimising noise in the workplace: eliminate or minimise it.
Assessment of plant, equipment and other sources of noise in operation at the workplace will help you identify machines that can be eliminated. You may be able to remove or shut down equipment or plant that are redundant or no longer necessary.
When considering substituting plant or equipment with quieter models, detailed consultation of noise emission information is required. Compare the data of similar equipment and choose the best supplier that can demonstrate a low noise design with noise control as a standard part of the machine, and not as an optional extra.
Plant and equipment can have modifications made or engineering controls applied to reduce the noise they emit. This requires assessing the following:
After checking these factors you can then draft a proposal which includes:
Be aware that factors, such as the environment around equipment and plant, may skew its noise emission data sheet. Nearby or surrounding walls or objects can reflect and amplify emitted sound. Using distance, barriers, enclosures and sound-absorbing surfaces are options that should be investigated and checked for feasibility, as they are often the least costly options.
Roots blowers are a common noisy type of plant used throughout the manufacturing industry. The use of a blower enclosures blower enclosurescan greatly reduce their noise level. Our soundproof blower enclosures, depending on site conditions, yield a significant noise reduction of 8 to 15 dBA.
We can achieve results down to 80 dBA. To get noise down to lower levels, however, may require us to engage specialist noise engineers to plan for dealing with possible complications, such as reflective sound from nearby surroundings. Pneuvay is able to offer expert advice when supplying blower enclosures to reduce workplace noise. Talk to us, today on 1300721458 or contact us. You can even send us a message via our Facebook page if you like.

Blower enclosures can help prevent noise-induced hearing loss
Get social with us and see the latest news items from:
Discover how we support the night Australian mining industry with our pneumatic conveying systems.
Read on for details about projects we've completed in Western Australia, Queensland, and South Australia.
Pipe and Tube Compression Couplings
Industrial Dust Collectors Systems
Dust Collectors Filters, Cartridges and Bags
Pneuvay Engineering Pty Ltd - Copyright 2020
ABN 49 006 027 541
